
Brazing is the process of joining two pieces using heat and a filler material that melts at a temperature above 427 ºC (800 ºF) and below the melting point of the parts to be brazen.
The filler material used in brazing varies depending on the parts being joined. The most commonly used alloys are phosphor copper, silver, nickel and cobalt, aluminium, silicon, copper, copper-zinc and magnesium.
The reason for this process between parts of the same or different materials is to create a permanent bond high strength, simplify mechanical operation and adopt simple production techniques, always compatible with the demands of mass production, among others.
There are different methods of heating for brazing, for example the flame, oven, infrared, laser and induction. Brazing by induction has a number of advantages over these other methods.
 Brazing of short circuit ring in rotor
Brazing of short circuit ring in rotor

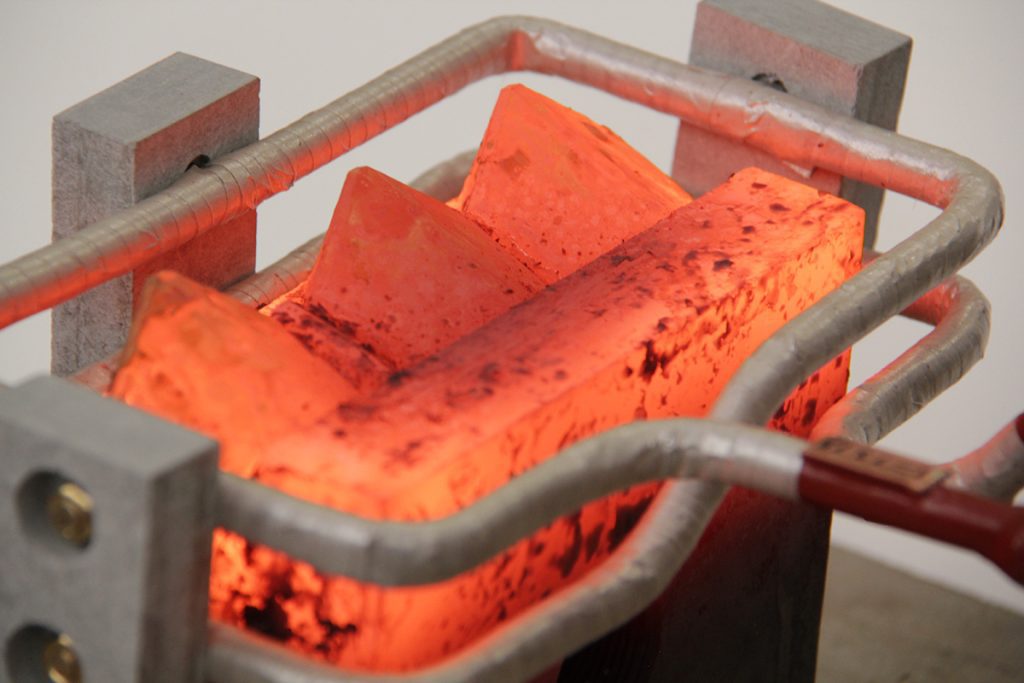 Brazing of carbide inserts
Brazing of carbide inserts

Download this guide to learn about the different aspects of brazing and the many advantages offered by this unique process.